Research: New Ideas and Instrumentation, Fundamental Plasma Studies, Molecular Analysis and Chemical Sensors, Elemental Mass Spectrometry Elemental Mass Spectrometry |
|
|
|
|
|
Mattauch-Herzog Geometry Mass Spectrograph Development of Plasma Source Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Elemental Mass Spectrometry through the Use of Hydride Generation |
|
|
|
|
| Mattauch-Herzog Geometry Mass Spectrograph | |
 |
 |
|
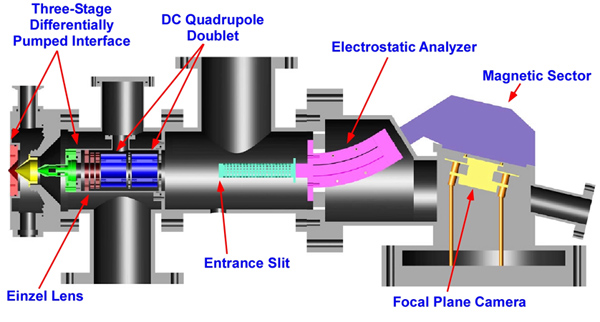
For an animated tour through the MHMS, Click Here! The Mattauch-Herzog geometry mass spectrograph (MHMS) has been coupled to several conventional ionization sources, such as the ICP, glow discharge, and electrospray ionization (ESI). Recently, molecular analyses have been achieved with the Mattauch-Herzog geometry mass spectrograph (MHMS) through the use of the (FAPA) ionization source. This combination marks the first detection of molecular species with the MHMS-FPC system. With the FAPA source, molecules are directly desorbed and ionized from solid surfaces. Furthermore, negative ions can be easily created when electronegative species, such as nitro groups from various explosives, are present. The MHMS-FPC system is easily converted to negative-ion mode by inverting all ion optic potentials and the magnetic field. No changes are necessary to the FPC. Active ingredients from pharmaceutical tablets and explosive standards have been analyzed with the negative ion FAPA-MHMS-FPC system. |
|
|
|
|
|
Development of Plasma Source Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry |
|
|
|
|
|
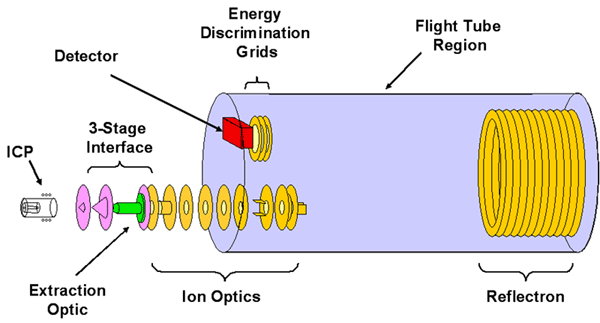
In contrast to scan-based mass analyzers, time-of-flight mass spectrometers (TOFMS) are capable of simultaneous multi-elemental analysis. Since all masses are extracted instantaneously from a plasma, greater measurement precision is gained through ratioing techniques. Because no slits are utilized, high transmission efficiency can result in enhanced sensitivity for ultra-trace analyses. The limited mass range of atomic analyses (0-250 amu) allows generation of complete atomic spectra at a rate exceeding 20 kHz. This high spectral generation rate makes TOFMS an excellent tool for transient samples (e.g. chromatography, laser ablation, electrothermal vaporization), reducing temporal and quantitative errors. Continued refinement of ion optical systems including collision cells, quadratic ion extraction systems and hybrid reflectrons will further enhance performance.
|
|
| Elemental Mass Spectrometry through the Use of Hydride Generation | |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
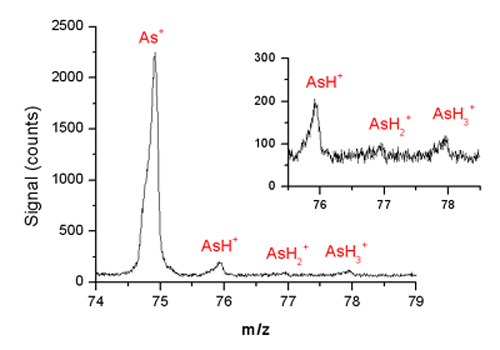
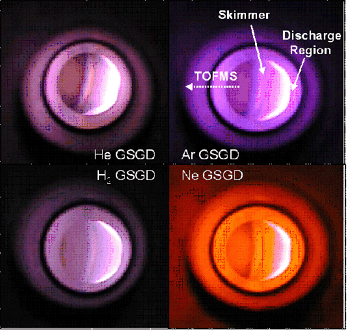
Since arsenic exposure can have adverse health effects, determination of these species is very important. Hydride generation is routinely employed to determine arsenic-containing species to remove matrix interferences. Only species that form volatile hydrides are sampled, so most of the sample matrix is removed. In our laboratory, a gas sampling glow discharge (GSGD) source can be sustained with a wide variety of working gases (helium, argon, hydrogen, and neon). The GSGD is used to atomize and ionize the arsine produced by the hydride-generation reaction, and these ions are then detected with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOFMS). The ratios of the hydride species (As+, AsH+, AsH2+ and AsH3+) give an indication of the robustness of the discharge. |
|
|
|
|